To CAcert.org Education & Training - To CAcert.org Education & Training Overview
CAcert.org Assurer Handbuch (incl. PracticeOnNames)
Da Übersetzungen im Allgemeinen nicht eins zu eins stattfinden können, kann dieses Dokument nur als eine möglichst gute Annäherung an das Orginal gestaltet werden. Ausschlaggebend ist immer das Originale Handbuch (z.Zt. in englisch). Des weiteren wird in der englischen Sprache nicht zwischen Du und Sie unterschieden. Daher wird in dieser Übersetzung durchgehend das Du verwendet, da davon ausgegangen wird, dass in einer Gemeinschaft des Vertrauens (Vertrauensnetzwerk = Web of Trust) die privatere Anrede zu vertreten ist. Um den Text einfacher lesbar zu gestalten, wird bei Personenbezeichnungen mal die männliche Form verwendet, mal die weibliche Form. Die andere Form ist dabei immer mitgedacht.
Meta Kommentare
Die Assurance Policy (englisch) hat den Status POLICY und ist somit gültig! p20090105.2 (englisch)
Dies ist das Trainings Handbuch für Assurance, genehmigt gemäß der Assurance Policy (englisch).
- Es ist ein Arbeitspapier für uns Assurer. Es wird wahrscheinlich ständiger Aktualisierung bedürfen!
- Bitte korrigiert und komplettiert es, damit es so bald wie möglich auch für neue Assurer nützlich ist.
- Ted hat hier schon einen gewaltigen Berg an Arbeit geleistet, um all diese Informationen zusammenzutragen.
- Das neue Assurer-Team um Ulrich, Joost, Ian, Dirk, Ted und Sebastian
- testen es auf Praxistauglichkeit und
- wollen ein lebendes Dokument daraus machen.
Du kannst helfen: Füge Kommentare in kursiv ein, wo Änderungen notwendig sind.
- Bitte beachten: Organisation Asurance (OA) hat ein eigenes Handbuch.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Contents
-
CAcert.org Assurer Handbuch (incl. PracticeOnNames)
- Meta Kommentare
- Einführung
- Der Vorgang des Bestätigens (Durchführen einer Assurance)
- The Standard of Assurance
- All about Names
- Practice on Names
- Signatures
- Dates
- Frequently encountered situations
- Verification and Measurement in the Web Of Trust
- Questions Answered
- Some more information on CAcert
- Some technical aspects
- Appendix
-
CAcert.org Assurer Handbuch (incl. PracticeOnNames)
Einführung
Dieses Handbuch ist für angehende und neue Assurer gedacht. Es soll einen ersten Anhalt geben, was zu tun ist und was man wissen sollte, wenn man als CAcert-Assurer handelt. Außerdem soll es ein Augangspunkt sein zu einem tiefern Verständnis bei speziellen Themen.
Zugehörige Dokumente
Die Dokumentation zur Assurance ist aufgeteilt zwischen Assurance Policy (AP) (englisch) und diesem Assurer Handbuch (AH).
Das Assurer Handbuch hat weitere praxisorientierte Unter-/Zusatzdokumente um die AP näher zu erläutern. Sollte dieses Handbuch oder eine der praxisorienterten Dokumente der AP widersprechen, so hat die AP Vorrang. Die Praxisdokumente sind auch wichtig für die Streitschlichtung (Arbitration).
Practice On Names (PoN) (ist mittlerweile Bestandteil dieses AH)
Practice on ID Checking (PoIDC)
Zusatzdokumente zur Assurance Policy (AP)
Policy on Junior Assurers / Members PoJAM (DRAFT)
TTP-Assisted-Assurance TTP-Assisted-Assurance (DRAFT)
Übergeordnete Dokumente
Obwohl dieses Dokument dazu gedacht ist, ihre "Assurer-Bibel" zu sein, gibt es dennoch einige wichtige andere Dokumente. Insbesondere:
Assurance Policy (englisch) (POLICY) ist das maßgebliche Dokument, welches das Assurer-System definiert. Sein Ziel ist es, eine Assurance so durchzuführen, wie sie für die Zertifizierung nach CPS (s.u.) gefordert wird. Es genehmigt dieses Handbuch als gültige, aktuelle Praxis.
Certification Practice Statement (CPS, englisch) (DRAFT; für die Community bindend) widerum ist das maßgebliche Dokument, wie ein Zertifikat auszugeben ist. Der Abschnitt 3.2.2. Authentication of Individual Identity verknüpft zu der Assurance Policy (s.o.) um zu zeigen, worauf sich die Mitglieder verlassen können, wenn sie ein Zertifikat nutzen.
Organisation Assurance Policy (englisch) (POLICY) ist ausschlaggebend für die Assurance von Organisationen.
Jedes Mitglied von CAcert (und damit jeder Assurer) ist an das CAcertCommunityAgreement (englisch) (POLICY) gebunden.
Einige Bemerkungen zu Grundlagendokumenten (POLICYS)
Dieses Handbuch ist kein Grundlagenpapier (POLICY), sondern eine Anleitung für die praktische Arbeit. Für den Fall, dass sich Widersprüche ergeben, haben die POLICYs immer Vorrang, deshalb sollte dieses Handbuch mit diesen Dokumenten konform sein. Sollten Sie Widersprüche finden, so gebe Sie diese bitte auf der CAcert Policy-Liste [ cacert-policy@lists.cacert.org ] bekannt.
Andere Grundlagenpapiere und Dokumente von CAcert können auf offizielle Dokumente (englisch) gefunden werden. Die Arbeit mit und die Entwicklung von Grundlagenpapieren ist definiert in Policy on Policy (englisch) und wird über CAcerts öffentliche Liste [ cacert-policy@lists.cacert.org ] geführt; jedes Mitglied kann der Liste beitreten und teilhaben.
Solange noch an den Dokumenten gearbeitet wird, bekommen sie den Status "in Arbeit" ( WIP -> work-in-progress). Wenn sie fertig bearbeitet sind, erhalten sie den Status "Entwurf" (DRAFT) und sind damit schon bindend für die Gemeinschaft (Community), müssen jedoch noch von CAcert Inc. genehmigt werden. Sobald sie genehmigt sind, erhalten sie den Status Grundlagenpapier (POLICY) und werden offiziell auf der gesicherten und überwachten Website https://www.cacert.org/policy veröffentlicht.
Alle Grundlagenpapiere habe Einfluss auf die Assurance, auch wenn dies dort nicht ausdrücklich erwähnt wird. Z.B. hat auch das Privacy Policy (englisch) eine Bedeutung für den Prozess.
Deine Obliegenheiten als Assurer
Du musst die Assurances durchführen, wie es die Grundlagendokumente regeln; insbesondere Assurance Policy (POLICY) (englisch).
- Du musst dich selber darum kümmern, die Änderungen der Grundlagendokumente mitzubekommen. Einige einfache Wege um über Änderungen informiert zu bleiben sind:
Einschreiben in die Mailingliste cacert@lists.cacert.org (Diese hat ein vergleichsweise geringes Mail-Aufkommen.
Besuche Ab und Zu CAcert Blog oder abbonniere den RSS feed.
Absolviere die AssuranceChallange CATS (CAcert Automated Training System) jedes Jahr mindestens einmal
Deine Risiken und Haftungen
Wenn Du CAcert beitrittst, akzeptierst Du die CAcert Community Agreement (CCA) (englisch). Darin werden die Risiken und die Haftung der CAcert-Mitglieder geregelt. Du solltest vertraut sein mit diesem Dokument, damit Du die Risiken und auch Deine Haftung verstehst und jedem potenziellen Mitglied darüber Auskunft geben kannst.
Dabei gibt es gute und schlechte Nachricht: Die CCA setzt beschränkt Deine finanzielle Haftung auf 1.000 EUR (eintausend Euro). Des weiteren akzeptiert jedes Mitglied die Schiedsgerichtsbarkeit von CAcert. Dies ist unser System, um Konflikte untereinander innerhalb der Gemeinschaft zu lösen, anstatt die Mitglieder auf Gerichte zu verweisen, die in fernen Ländern liegen können und damit teure Anwälte erfordern und/oder eine Gerichtsbarkeit haben, die nicht voll abschätzen kann, worum es bei Zertifikaten geht. Die Haftungsgrenze ist innerhalb der Gemeinschaft ausgewogen, da sie für Dich gilt, wie für jeden anderen der einen Streitfall mit Dir hat; damit ist es beides, ein Maximum an Schutz für Dich und eine Obergrenze für Deine Haftbarkeit.
Daher solltest Du immer sorgfältig vorgehen, wenn du jemanden bestätigst (eine Assurance machst), denn Du kannst bis zu diesem Limit von einem Schiedsmann von CAcert verantwortlich gemacht werden!
Der Vorgang des Bestätigens (Durchführen einer Assurance)
Der Vorgang des Bestätigens ist ein entscheidender Teil des CAcert Projekts. Solange die Bestätigungen in einer verlässlichen Art und Weise durchgeführt werden, können sich die Mitglieder voll und ganz auf die Zertifikate von CAcert verlassen. Wenn jedoch die Bestätigungen oberflächlich gemacht werden, geht diese Verlässlcihkeit verloren und das Projekt wird scheitern. Also hängt alles von Dir ab!
Das im folgenden beschriebene Vorgehen ist ein Vorschlag. Du kannst die Vorgehensweise ändern, aber dann musst Du sicherstellen, dass bei Deinem Vorgehen die Bedingungen der Assurance Policy (POLICY) (englisch) !! erfüllt sind.
Gib Dich als CAcer Assurer zu erkennen
Der wahrscheinlich einfachste Weg ist es, in Deinem Profil einen Ort einzutragen und zu erlauben, das Dein Eintrag in der users Liste angezeigt wird. Andere Möglichkeiten zu finden, wie z.B. Deine Freunde und Bekannte zu informieren, bleiben Dir überlassen.
Bestätigungen innerhalb des Web of Trust ist keine Einbahnstraße, daher solltest Du ein Minimum an Informationen wie Deine Email-Adresse und Deinen Namen mitteilen. Zm Beispiel auf der Visitenkarte. Siehe auch Gegenseitige Bestätigung.
Empfohlene Vorbereitung für eine Bestätigung
Nehmen wir einmal an, jemand hat mit Dir Kontakt aufgenommen und bittet Dich, ihre/seine Identität für CAcert zu bestätigen. (Es gibt auch andere Wege eine korrekte Bestätigung durchzuführen, doch die folgende ist eine gute erste Variante).
Drucke ein vorausgefülltes CAP-Formular aus
Als allererstes solltest Du überprüfen, ob der Interessent schon einen Account bei CAcert hat. Dazu gehst Du nach https://secure.cacert.org/wot.php?id=5 und gibst die EmailAdresse ein, die Dir der Interessent angegeben hat. Wenn diese Adresse korrekt war, bekommst Du ein interaktives Bestätigungsformular angezeigt. Auf keinen Fall jetzt schon etwas in dem Formular ändern!!, benutze nur einen der Links in der Bodenzeile, um ein vorausgefülltes CAP-Formular als PDF-Dokument zu öffnen und anzudrucken.
Wenn die Emailadresse im System nicht gefunden wird, dann frage den Interessenten nach seiner primären Adresse für den Account.
Das aktuelle CAP-Formular ist unter https://www.cacert.org/cap.php (englisch) zu bekommen.
Ein weiterer Vordruck ist unter https://www.cacert.org/capnew.php (englisch) zu finden, dies enthält mehrere Zeilen für unterschiedliche Namensvariationen bei unterschiedlichen Dokumenten.
- Am einfachsten ist ein CAP-Formular in deutsch zu bekommen, wenn Du Dich bei CAcert einwählst und dort den entsprechenden Link anklickst.
Bei der Bestätigung sollte die erste Frage an die Interessierte sein:
- Haben Sie einen Account bei www.cacert.org?
Notier Dir bitte die Antwort am besten irgendwo auf dem Formular z.B.
- [+] Account existiert
- [-] Account existiert nicht (siehe unten 'Ausstehende Kontoerstellung')
Wenn die Antwort 'JA' ist,
- frage nach, ob die angegebene Email-Adresse die primäre Email-Adresse der Interessentin ist.
Wenn die Antwort 'NEIN' ist,
- gehe weiter vor, wie es hier im Kapitel Bestätigung von Nicht-Mitgliedern beschrieben wird.
Bestätigen von Nicht-Mitgliedern
Wenn die Interessentin noch kein Konto erstellt hat, wirst Du sie nicht in unserer Datenbank finden. In diesem Fall, die Interessentin ist noch kein Mitglied, solltest Du sie bitten, ein Konto anzulegen und Mitglied zu werden, bevor Du sie bestätigst.
Unter bestimmten Bedingungen, wie z.B. eine Massen-Bestätigung auf der CeBIT oder ein zufälliges Treffen, kann es sinnvoll sein, die Bestätigung schon durchzuführen, bevor die Interessentin ein Mitglied ist. Wie auch immer, es sollte möglichst vermieden werden, da einige Sicherheits- und auch juristische Gefahren bestehen, wenn die Person zuerst bestätigt und das Konto erst später angelegt wird. So hatte die Interessentin nicht genügend Zeit, das CAcertCommunityAgreement (englisch) zu lesen, was sie einfacher am Bildschirm oder später machen sollte. (Denk daran, dass bei Events immer einige Kopien der CAcert_CCA_DE zum mitgeben da sind.)
Auf jeden Fall solltest Du in der Lage sein, der Interessierten einen kurzen Überblick über die beiden wichtigsten Punkte in der CCA zu geben:
- Das sie an die CAcert-eigene Schiedsgerichtsbarkeit gebunden ist (CCA 2.1 Risiken, CCA 3.2 Arbitration als Forum für die Schiedsgerichtbarkeit)
- Das eine mögliche Haftung begrenzt ist auf 1000 € (eintausend Euro) (CCA 2.2 Haftung)
Vorgeschlagener Ablauf: Für den Fall, dass Du Dich entscheidest weiterzumachen und ein Nicht-Mitglied zu bestätigen bevor sie ein Konto erstellt und/oder der CCA zugestimmt hat, richte Dich nach der folgenden Vorgehensweise um Dich und das Nicht-Mitglied zu schützen:
Das zukünftige Mitglied kreuzt den Satz "Hiermit stimme ich der Vereinbarung der CAcert-Gemeinschaft (CCA) zu." oberhalb der Unterschrift an,
du markierst das Formular als Kontoerstellung geplant,
du gibst ihr eine Kopie der CAcert_CCA_DE und sagst ihr, wo sie zu finden ist,
gib ihr Deine Email-Adresse, damit sie Dich anweisen kann, das Formular zu vernichten, wenn sie sich entscheiden nicht zuzustimme und kein Mitglied zu werden.
Auf diesem Weg zeigst Du an, dass das zukünftige Mitglied später Zeit hat, die CCA zu lesen und bei der Kontoerstellung wird sie ihre Zustimmung bestätigen. Wenn das Konto nicht erstellt wird, ist die Zustimmung null und nichtig und du kannst das Formular entsprechend markieren oder direkt vernichten. Zwischenzeitlich habt ihr aber beide zugestimmt, die Bestätigung unter den Bedingungen von CAcerts Grundlagendokumenten und den entsprechenden Verfahren zur Streitbeilegung durchzuführen.
Informiere Dich über die Dokumente, die die Anfragende vorzeigen möchte
Du solltest die Interessentin fragen, welche Identifikationsdokumente sie vorlegen will. Weise sie darauf hin, dass Du mindestens einen (besser sind zwei!) Identitätsnachweis mit Bild im Original sehen musst von denen dann mindestens einer von einer Behörde ausgestellt sein und das Geburtsdatum beinhalten muss. Wenn sie ungewöhnliche oder ausländische Dokumente vorlegen will, informiere Dich bitte im voraus, wie diese Dokumente aussehen müssen. Du kannst die Seite Anerkannte Dokumente (englisch) als Ausgangspunkt für die Suche nehmen.
Du solltest die Interessentin auch bitten das Ablaufdatum der Dokumente zu kontrollieren, damit Du nicht in die Verlegenheit kommst, entscheiden zu müssen, ob die evtl. abgelaufenen Dokumente gültig sind.
Plane das Treffen
Du musst die Interessentin persönlich treffen (von Angesicht zu Angesicht). Keine Bestätigung am Telefon, noch nicht einmal über Videotelefonie! Daher müsst Ihr einen Treffpunkt ausmachen. Wenn Dein Arbeitgeber damit einverstanden ist, wäre Dein Arbeitsplatz ein guter Treffpunkt. Natürlich könnt ihr Euch auch bei Dir zu Hause treffen, wenn Du das möchtest. Ansonsten solltet Ihr einen Ort wählen, der nicht zu belebt ist.
Nimm das vor ausgefüllte CAP-Formular mit und vergiss nicht einen Kugelschreiber mitzunehmen, Die Interessentin muss das Formular noch unterschreiben.
Das Treffen
Bitte stelle sicher, das Du während des Treffens nicht unter Zeitdruck stehst. Du solltest mindestens fünf Minuten ansetzen, um die Dokumente zu prüfen und die Interessentin das Formular unterschreiben zu lassen! Lass Dir Zeit.
Schüttle der Interessentin die Hand und schenke ihr/ihm vielleicht ein Lächeln. Gib dem Mitglied, wenn möglich, eine Visitenkarte mit Deinem Namen, Deiner Email-Adresse und deiner Bezeichnung als Cacert-Assurer. Dies kann auch handgeschrieben sein. CAcert ist eine Gemeinschaft, keine Firma.
Checkliste
Dinge, die Du überprüfen solltest:
- Die Daten auf den Dokumenten (Name und Geburtstag) stimmen mit denen des CAP-Formulars überein.
- Frage, ob der Account schon angelegt ist.
- Frage, ob die Email-Adresse auf dem CAP-Formular die primäre Adresse ist. Ist dies nicht klar, schreibe Dir die alternativen Email-Adressen auf.
- Kontrolliere, ob auf dem CAP-Formular die Zustimmung zur CCA oberhalb des Unterschriftfeldes eingetragen ist. Wenn die Zeit es erlaubt, mache der Interessentin klar, was diese Zustimmung bedeutet (Verantwortung und Schiedsbarkeit). Vielleicht kannst Du ihr einen Ausdruck der CCA aushändigen.
- Lasse die Interessentin das CAP-Formular unterschreiben.
- Vergleiche die Person mit der auf den Dokumenten.
- Notiere Dir die Art der Dokumente, die vorgezeigt wurden (z.B. Personalausweis, Führerschein, Reisepass) und mögliche Namensvariationen (zusätzliche Vornamen, akademische Titel, Geburtsname) die in den Dokumenten auftauchen. Wenn die Namen auf einem Dokument sich von denen auf dem (vorgedruckten) CAP-Formular unterscheiden, kopiere den Namen vom Dokument so genau wie möglich auf das CAP-Formular. ‚‘‘‘Das CAP-Formular ist Dein einziger Beweis für das, was Du gesehen hast!‘‘‘
Bezüglich Namen und Namensteilen:
Akzeptiere nur Namen oder Namensteile (z.B. Titel), die Du gegen ein offizielles behördliches Dokument mit Bild prüfen kannst.
Einige Punkte die Du beachten solltest:
- Fotos/Bilder
- in einigen Ländern läuft der Führerschein nie ab, so musst Du hier auf sehr alte Bilder und Unterschriften gefasst sein.
- Unterschrift
- Es ist wünschenswert, dass die Interessentin die Unterschrift vor den Augen des Assurers (also Dir) macht.
- Wenn das CAP-Formular schon unterschrieben ist, bitte die Interesentin, es an einer anderen Stelle noch einmal zu unterschreiben, während Du zusiehst.
- Sollte die Unterschrift unleserlich sein, bitte die Interessentin die Unterschrift vergleichbar mit dem Dokument zu leisten.
- (manchmal ist es eine neuere Bank-Karte ein guter Hinweis, wenn die Unterschrift gravierend abweicht, jedoch ist es verboten, Details von der Bank-Karte abzuschreiben. Halte deshalb die Finger über die sensiblen Daten oder bitte sie, diese selbst zu verbergen)
- wenn ein vorgelegtes Dokument nicht unterschrieben ist, bitte die Interessentin, es jetzt zu unterschreiben. ‘‘Ob das sinnvoll ist, eine gefälschte Unterschrift zu erkennen, ist aber fraglich‘‘
- Sicherheitsmerkmale
- Das Siegel muss auf Bild und Dokument genau aneinanderpassen.
- Hologramme
- Spezielle Drucktechniken wie ‚fine Print‘ oder Farben
- Spezialpapier
- Die Klartextinformationen auf dem Dokument sollten mit den maschinenlesbaren Teilen des Dokuments übereinstimmen
- Wasserzeichen
- Ablaufdatum
- in manchen Ländern gibt es für Führerscheine kein Ablaufdatum
- Personalausweise hat normalerweise eins von 10 Jahren
- abgelaufene Dokumente können akzeptiert werde, du kannst dann die Punkteanzahl die Du gibst vermindern
- Du solltest die Interessentin darauf hinweisen, dass das Dokument bald ungültig wird
- Sind Ausgabe- und Ablaufdatum sinnvoll und ergeben eine sinnvolle Gültigkeitsdauer (z.B. 10 Jahre), Ausgabedatum und Ablaufdatum müssen sich um mindestens einen Tag unterscheiden (z.B. 15. Juni und 14. Juni
- Geburtsdatum
- Date of birth
- don't get confused by the different formats all over the world. Check your input twice if the formats are the same on the form, the documents and the web interface. If the date in the web interface is wrong, it must be changed BEFORE you can give the points. File a dispute to get it changed.
- does the member seem to be around that age?
- consider rewriting it in your own writing if the Member's version is ambiguous
Note the numeric month in character short month format (this helps to reduce DoB errors about 50 % !!! don't ask why?
 )
)
- Names! The Assurance works with Name variations.
- Write down any additional names on the form.
- The online account should include the longest and fullest form of the name possible.
- The Assurance is over one or more Names. Carefully write down each name variation fully on the CAP form against the document that it is found on.
- Often you will find the Name on the CAP is different to the name on the ID documents, and again the online web interface is different again. Discuss with the Member what the best form of the name should be, and consider filing a dispute to get the online web interface name changed to the best form.
- artist names are officially-recognised alternate names that a person in an artistic field uses. As they are supported by the documents, they can be Assured.
- consider rewriting it in your own writing if the Member's version is ambiguous
- remember about the short rule: Allow only names or name parts (i.e. suffixes) that you can verify at least against one govermental photo ID
- in general: its allowed to reduce information, but it is prohibited to add informations
- often bonafide members gets encouraged to enter their title as suffix in the Join form and find the samples on the linked wikipedia site, but these titles aren't in any govermental photo ID. So these suffixes cannot be assured. Not in the face-2-face meeting, nor later on the online form.
- Test Questions:
- place of birth
- place of issue
Note that unique numbers on Identity Documents should not to be stored due to problems with liability and the potential to cause ID theft.
For names or name parts:
- in general: its allowed to reduce information, but it is prohibited to add informations
CAcert Assurance vs. Pure Id Document Check
- CAcert's Assurances has a wider purpose
Purpose of Assurance
Pure Id Document Check
CAcert Assurance
Member
Check for Account
Account
Check Primary Email
Certificates
Check Arbitration Acceptance
Arbitration
Disclose R/L/O
Check CCA AcceptanceSome Data
Id Document Check
Id Document Check
Disclosure of R/L/O -> Risks, Liabilities, Obligations
Risks -> You may find yourself subject to Arbitration
Liabilities -> limited to 1000 Euro
Obligations -> to keep your primary email in good working order
Things to discuss
Have a little chat with the applicant, if time permits and both parties are interested. ![]() As a representative of CAcert, you the Assurer may find yourself helping the Member in wider aspects of the Community. Some general things to discuss are:
As a representative of CAcert, you the Assurer may find yourself helping the Member in wider aspects of the Community. Some general things to discuss are:
- What it means to be a Member. In 2007, the Community became more organised with the introduction of the CCA. Members agree to that document, although like all contracts and legal blah blah, it is likely that the new Member has not read it all or understood it all. You as Assurer have read the CCA, and can introduce some important ideas to the new Member.
The Assurance covers the 5 points listed in "The Assurance Statement" of the AP. It is not just a check of Identity.
- Security and Obligations. In CCA there are a set of obligations which can be discussed: things like looking after your private keys, and understanding the difficulties of modern virus-ridden platforms, complicated websites and script-driven browsers.
Arbitration and dispute resolution. As a Community, we resolve our disputes internally. For some people this is scary, as they believe in the protection of their own courts. It is often good to point out why Arbitration works for CAcert: in the international context of the Internet, Arbitration means we can protect the Member from disputes in far away places. See the section on Arbitration in this Handbook, and DRP's last section for more discussion on this.
What the Member wants to use certificates for. It is generally hard to figure out how a lot of technology is used in the field, and meeting someone is a good time to get a view. As a user, the person finds difficulties and experiences that the more technically-oriented people are blind to. This is your chance to listen to user experiences, and think strategically about how to improve her security.
- Helping CAcert: Try to find out, in which area the Assuree has skills. What hobbies he has. What kind of job he is doing. CAcert searches for volunteers in many places: Assurers, Events, Presentations, Support, Documentation, System administration, Development, Deployment, Arbitration, Communicators, Consultants, Managers ... make a note on the CAP form for which area the Assuree is interested in and forward the contact details to the appropiate team leader by CC'ing the Assuree to the email you'll send.
If you do get a chance to discuss anything with the Assuree, it is good to make a small note on the CAP form about what it was.
After the meeting
If you did notice anything unusual, make some notes on the backside of the CAP form. Things you should note include (but are not restricted to):
- very unusual documents
- very old or worn documents
- if something "just didn't feel right"
- the applicant tried to hurry you through the process
- Something unexpected did happen
Those notes might help you to remember what happened later, just in case a dispute is filed and someone asks you about details of the meeting.
Issuing Assurance Points
Now login to the CAcert website, go to https://secure.cacert.org/wot.php?id=5 once again and enter the applicants email. Now fill out the assurance form, check the data once again and issue your points if there are no reasons against. If the situation was not ideal you should give less points, see Assurance/PracticeOnIdChecking for some guidelines about the number of points to give.
The meaning of the Assurance Points is your expression in the confidence of the Assurance Statement. If you are completely sure, issue maximum points. From AP4.3, completely sure means:
- Detail on form, system, documents, person in accordance;
- Sufficient quality identity documents have been checked;
- Assurer's familiarity with identity documents;
- The Assurance Statement is confirmed.
If the documents look good but are unfamilliar to you (like foreign documents), you may decide to issue partial points (although some Assurers choose to issue only maximum or none).
There are two special cases: if you have no confidence in the Assurance Statement, then issue zero points. This will most often occur if the documents are totally unfamiliar to you. For example, a Finnish driver's license presented to an Australian Assurer at an event in Chile! The documents mean nothing to you, but as you have still made a good faith attempt to do the Assurance, it is good to record that fact. It is still worth experience, and your CAP form is still a good record. Advise the Member that this may happen, and the reasons why, so as to maintain good faith.
The second special case is if you have negative confidence. That is, you think there is something wrong, such as some of the documents are false or inconsistent. In this case, do not complete the Assurance (do not sign the form and do not press the "I am sure of myself"-Button on the web application), but instead consider filing dispute.
Remember the following issues:
- do not log in from a Computer which is not secure (possibly has any malware like viruses and trojans on it).
- do not use other people's computers unless you are sure that you can trust them. If in doubt do it from a Live-CD like knoppix.
use an up-to-date browser and go to https://www.cacert.org/.
FOR SECURITY REASONS: LOGOFF AND CLOSE THE BROWSER WHEN WORK IS DONE.
- If someone tried to use faked IDs or otherwise tried to obtain an assurance by fraud, file a dispute by emailing support at c.o.
What about that CAP form?
As well as the Assurance details (Name, primary email, DoB), the CAP form (short for CAcert Assurance Programme form) must contain AP4.5:
applicant's signature made by his/her own hand.
- applicant's permission to conduct the Assurance.
- applicant's acceptance of the CCA and thus the risks, liabilities and obligations of membership.
- Your Name
- Assurance points you allocate
- you CARS:
- you agree to the CCA,
- you are an Assurer (have done CATS Challenge, have 100 Assurance Points),
- that you have conducted the assurance to Assurance Policy,
- all covered by your signature.
- Date and location (reminder) of the Assurance
For the old-style one-way Assurance, cross out the fields for your email address and Date of Birth, as desired. (Note that we are now preferring the mutual Assurance where possible.)
Mutual Assurance. For a mutual Assurance, fill them in (or use two CAP forms). If the other Member is not an Assurer as yet, then
- if the other Member is unsure, you may keep the CAP form(s) on her behalf (and take responsibility for both Assurances) which is why the form itself has both sets of details on it.
- if the other Member is about to become an Assurer, or you otherwise judge the Member is capable of meeting the storage requirements, then she may keep her CAP form recording her Assurance over you.
Storage. The Assurer has to securely keep the paper CAP form for at least seven years. You are personally responsible for this (and in the mutual assurance with a non-Assurer, you remain responsible!) ! It is your evidence that you have followed CAcert's Assurance Policy and that you met the applicant in person (face to face).
For data protection and privacy reasons no-one else should have access to the CAP forms, once completed. Do not scan the CAP form and keep it electronically. CAcert's Assurance is deliberately designed to create a paper foundation on which digital certificates are issued; by maintaining a base of paper, the digital framework is strongly constructed with a classical legal foundation. Not only does scanning weaken that foundation, you may also violate data protection laws on electronic data storage.
In the case of a dispute you may be requested to send the original paper form to a CAcert Arbitrator. See below for more details.
If you find yourself unable to keep the CAP forms for whatever reason, file a dispute at support@cacert.org, explain the circumstances, and request the Arbitrator to provide instructions.
Sending CAP forms to CAcert by request
An Arbitrator may request you to send him the CAP forms, maybe because there was a complaint about a certificate or just as part of a quality assurance process. CAP forms contain personal data, so the requester has to be authorized to see them and you have to make sure that no-one else can read that data.
- Verify that the requester's email is @cacert.org. No other TLD (like .com, .net etc) is allowed!
Verify that the requester is an Arbitrator or Case Manager for a case relating to the person who has signed the CAP form. Current Arbitration cases are listed at ArbitrationCases, the Arbitrator/Case Manager should have stated the case number in her request.
- The request will be sent to you either signed by a CAcert verified PGP key or using a CAcert-issued S/MIME certificate. Please ensure that the certificate is valid and issued/signed by CAcert.
If you do not know how to reliably verify a signature please ask someone for help on on IRC (irc://irc.cacert.org/cacert or irc://irc.cacert.org/cacert.ger) or one of the mailinglists (like mailto:cacert@lists.cacert.org or mailto:cacert-de@lists.cacert.org). This is not a trivial task, don't just trust your mailer's icon!
- Usually you will be requested to send a scan of the CAP form. Please make sure that you send the image using an encrypted mail. If you cannot send it encrypted for any reason, send a copy of the form via paper mail. After you confirm receipt of the scanned CAP form, delete your digital copy carefully.
If you are requested to send in the original CAP form, keep a copy of it in your documents. N.B.: I have not heard of this being requested, but it may be necessary some time.
If you have any doubts about a request ask for help. Once again, try IRC or mailing list(s)! If the request tries to discourage you from getting help (stating it a top secret business or something like that) there's something fishy about the request!
Fees
- Certificates are free! Customers create them themselves using the web interface.
Assurances may cost money but the price has to be set out before the meeting. Otherwise it must be done at no charge.
- If you choose to demand money for the assurance, keep it to a sensible amount of "expense recovery". If the applicant visits you, something between 5 and 15 EUR seems sensible in central Europe. If you visit an applicant yourself you may add travel expenses.
- Note: if you demand money for the service of assurance this may make you a commercial service provider, which, in turn, may have other legal consequences (like paying taxes, the need for a trade license or such things), depending on the laws of your country.
Assurance Events
You may be asked to be an Assurer at an Event. Have a look at EventOrganisation. This is a great opportunity to build up experience as an Assurer because you will be working with other experienced people, and you can discuss all sorts of issues and difficulties. This should also be reflected in your Experience Points!
The Standard of Assurance
IMHO this paragraph still needs some work to be less confusing for newbie (and experienced) assurers. The CAP links to this handbook for a definition of the "Standard of Assurance", so it has to be done. I'm still thinking about it, if you have an idea feel free to propose it. BernhardFröhlich
Also, see Assurance Policy (POLICY) ... which should nail down the Standard of Assurance ... once and for all ![]() iang.
iang.
AP5 puts the responsibility of the standard of assurance on the Assurance Officer, stating that this role includes:
Maintaining a sufficient strength in the Assurance process (web-of-trust) to meet the agreed needs of the Community. |
The customary standard includes these points:
- For a full-points Assurance, at least one government-issued photo ID containing the name and date of birth must be verified by the Assurer.
- Acceptable forms include Passports, Drivers Licenses and National Identity Cards.
This may be customary - and even preferred - but does not actually match up with AP - as far as I can see, the only requirement is for the name to be in the photo-ID doc (AP 2.1) and that "Sufficient quality identity documents have been checked" (AP 4.3). As far as I can see the DOB in photo ID requirement is not mentioned specifically elsewhere in either AP or Assessors Handbook!
- It is required that the date of birth is validated, but, as far as I can see, that can legitimately be done from other documents (such as a birth certificate) provided the name matches. (There may be an issue here if someone has had a name change (eg on marriage) but I believe that provided there is a "chain of evidence" that is examined (ie the document causing the name change) this ought to be acceptable)
This is particularly relevant in countries that have either no formal national ID or have many that could be regarded as acceptable! Alex Robertson
We do not want to repeat the AP here. Here we want to give simple procedures which remain "on the safe side" of the AP. The list of documents is not complete, and constantly expanded at AcceptableDocuments, but these are the most common ones. If you deviate from these procedures you should take care of documenting very comprehensible (sometimes Arbitrators can be really dumb!) why you were sure that the document you checked met the requirements of the AP. BernhardFröhlich
- Acceptable forms include Passports, Drivers Licenses and National Identity Cards.
- For a Name to appear in a certificate, the Member should have been verified by at least two Assurers.
- Exceptions see below in "Major Variations".
Your Assurance is a CAcert Assurer Reliable Statement, or CARS. This means that anyone in the community may rely on your statement.
Minor Variations
An Assurer may control minor variation, such as poor quality ID or missing ID, by reducing Assurance points.
It would be extremely unusual to issue full points if the Member does not have a good government-issued photo ID. On the other, such an ID does not mean full points; look at the additional documents to confirm.
Major Variations
Four Major Variations exist to the above
the TTP programme, see TTP. (New program under deployment)
the Super-Assurer programme, see SuperAssurers. This programme is administered by the board and can result in an Assurer getting more experience points temporarily. Terminated Permanently in April 2009.
Tverify, which takes certificates and other information from other CAs. Terminated Permanently on 16th November 2009.
the Organisation Assurance programme, see OrganisationAssurance.
All about Names
Name Matching
The relevant policy text for name matching is Chapter 2.1 and 2.2 of the Assurance Policy. More specific information as well as many examples can be found at PracticeOnNames.
Transliterations
Usual transliterations, missing accents and similar things are accepted. So if the ID doc says "André Müller" but the name in the account is "Andre Mueller" that's OK.
Note that the reason for accepting plain ASCII representations of non-ASCII characters are usual restrictions of computer environments. Therefore it is not accepted to assure someone as "Müller" if the ID documents contain "Mueller".
Still it's not well defined how names of other character sets (like for example Chinese or Hebrew) should be handled. The Assurance Policy encourages using exact representations in unicode, but allows transliterations. Transliteration rules can be found at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transliteration
Case Sensitive - Case Insensitive
Following was from the Assurance Policy work, for consideration now in the Handbook:
[[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transliteration|Transliteration]] of characters as defined in the transliteration character table ([[http://svn.cacert.org/CAcert/Policies/transtab.utf|UTF Transtab]]) for names is permitted, but the result must be 7-bit ASCII for the full name. Transliteration is one way and is towards 7-bit ASCII. Transliteration is a way to compare two names. However transliteration of a Name makes the Name less discriminative. In general names are handled case insensitively. Abbreviation of second given name(s), middle name(s), titles and name extensions in the name of an individual to one character and the dot indicating the abbreviation, is permitted. If the first given name in the ID document is abbreviated, the first given name in the web account Name may be abbreviated. Abbreviation of a name makes the name less discriminative, so it is deprecated. A Name on an ID which has initials (abbreviations) for titles, name extensions and given names, and/or transliterations as defined in the transliteration table can be taken into account for assurance for a Name in the account which is not abbreviated or transliterated. Titles and name extensions in the name of an individual may be omitted. The assurance ambition is to pursue a highly discriminative assured Name in the account. The ambition is to have only a Name in the account which has no abbreviation(s), no transliteration and is case sensitive.
End of insert from WiP-AP.
Arbitration case a20090618.13 Opinion
Naming and the writing of names is a complicated subject that follows different rules in different cultures. Even within a culture there is a multitude of difference in how names may be spelled.
Capitalization is the subset of name spelling at issue here. There are a multitude of countries in which the script used differs wildly from western letters. In such scripts capitalization may not even exist. Names that are transliterated from such scripts would then have an arbitrary capitalization, since who is to say which parts of such a transliterated name are capitalized.
The claimant has himself stated that often times names in official documents are spelled in all capital letters although the name would generally be spelled with an initial capital letter followed by letters in lower case. So it is evident that even within the culture of the claimant capitalization rules for names (especially when taken outside the context of sentences) are unsettled.
However there are instances where capitalization of names does make a difference. As an example one can think of McCain or DeHaviland. Both names are properly spelled with a capital letter at the beginning and the interior of the name. Capitalizing correctly here may alter the name significantly at least within the culture of origin.
As a result naming and name capitalization is not something that can easily be prescribed.
However at question here is really whether an assurance of a name spelled with unusual capitalization is permissible. In order to answer that question one only needs to look at the Assurance Policy, which states:
1. Assurance Purpose The purpose of Assurance is to add confidence in the Assurance Statement made by the CAcert Community of a Member. With sufficient assurances, a Member may: (a) issue certificates with their assured Name included, (b) participate in assuring others, and (c) other related activities. The strength of these activities is based on the strength of the assurance. 1.1.The Assurance Statement The Assurance Statement makes the following claims about a person: 1. The person is a bona fide Member. In other words, the person is a member of the CAcert Community as defined by the CAcert Community Agreement (CCA); 2. The Member has a (login) account with CAcert's on-line registration and service system; 3. The Member can be determined from any CAcert certificate issued by the Account; 4. The Member is bound into CAcert's Arbitration as defined by the CAcert Community Agreement; 5. Some personal details of the Member are known to CAcert: the individual Name(s), primary and other listed individual email address(es), secondary distinguishing feature (e.g. DoB). The confidence level of the Assurance Statement is expressed by the Assurance Points.
Specifically at issue is item 5 of the Assurance Statement, because the question is whether a name "is known" to CAcert if the capitalization is arbitrary and potentially different from the presented Identification Documents. In other words:
If I tell you that my name is "philipp dunkel" do you then know my name?
In this specific case I would answer that question with yes. However that is a judgment call that will depend highly on the name and culture at issue. Throughout the Assurance Process the Assurer should be guided by their own sound judgment. In fact the entire system of the CAcert Web of Trust is based on us trusting an Assurers judgment. Since none of the items mentioned in point 3.1 of the Assurance Policy as guidelines resolve the issue of capitalization the Assurer is allowed, or in fact required, to use his own judgment.
So on the question of whether the claimant may complete this Assurance as requested in the original claim:
- There is nothing that would explicitly prohibit this Assurance from being completed at this time.
- However whether the Assurer feels confident that CAcert knows the Assurees name given the capitalization, he will have to use his own judgment.
Middle names and Initials
According to the AP it is preferred that all given names which can be verified in one of the ID documents are recorded in the account.
If a person has multiple given names (or middle names) at least one given name must be used in the account unabbreviated. Additional names may be omitted or abbreviated, usually to the first character with or without a dot to indicate the abbreviation.
So someone called "Bernhard Andreas Fröhlich" may create his account as "Bernhard Fröhlich", "Andreas Fröhlich" or "Bernhard Andreas Fröhlich". Initials are deprecated, but are currently tolerated, so if the said person would use the name "Bernhard A. Fröhlich" this would currently be OK.
But remember, you may not assure an Account with a name you did not see on at least one ID document! If all ID docs state "Bernhard Fröhlich", assuring him as "Bernhard Andreas Fröhlich" is prohibited!
If the name on the presented ID documents is not identical to that on the CAP form it is the best to note the name as exactly as possible somewhere on the paper, including all given/middle names. If the account is disputed later then you can remember the exact name you've seen.
Multiple Names, Pseudonyms
According to the Assurance Policy (POLICY), multiple names are accepted, if matching ID documents can be presented.
Currently the CAcert software cannot handle them, but if you note them on the CAP form you can assure them later once the feature is implemented.
Practice On Names
To CAcert.org Education & Training - To CAcert.org Education & Training Overview
To Assurance Policy - To Assurance Handbook
česky | english
Practice on Names
Currently this is an interpretation based on the Assurance Policy at http://www.cacert.org/policy/AssurancePolicy.php#2.1 to specify more clearly how to match names found in official ID documents with names stored in CAcert accounts.
It is intended to be a bit on the safe side and might be more restrictive as the policy itself. Also the interpretation concentrates on "western names". Though some thought has been given to other regions, it might be not suited well to special situations. If you encounter such a situation, feel free to explain it on the Education mailing list.
Non-policy Notes:
This probably belongs in the Assurance Policy.
This needs a linkage from Assurance Handbook that clearly explains what are the rules, how much we can rely on this document. I.e., either this document is acceptable and approved practice in Names variations as per AP, or it is ... not!
There were some discussions on -policy about this during April which should be considered first. [samj]
There needs to be a linking into the CPS on how the Names are used.
This document is now part and included in the Assurance Handbook
General Standard
It is preferred that the name used in the account can be matched exactly to the name as written in at least one government-issued Identity document.
For several reasons some deviations of this preferred standard are accepted.
Basic, Simple, Strict Rules
We assure only names, that we can find in at least one ID document.
We assure only names, that we can find in at least one ID document.
Its allowed to reduce information, but its prohibited to add information. (The data of the ID documents does not have to be used completely, that is not all given names have to be used and names may be abbreviated under certain circumstances.)
Its allowed to reduce information, but its prohibited to add information.
Always document missing names on the CAP. (A person may have multiple names as long as they are verifiable with official ID documents)
Document missing names on the CAP.
Transliterations are accepted because of technical reasons (8bit to 7bit conversions)
Transliterations are accepted
We use Case-Insensitive
Case-Insensitive
Clarifications
- It is always preferred to have the name(s) in the account exactly like the name(s) in the ID documents.
Translations of names (Matthew <-> Matthias) are not accepted (Reason: it is too complicated to verify translations)
- Initials of first and middle names are depreciated but accepted (Reason: Rule #2, but this may be open for discussion. Maybe at least one given name should be used completely?)
- Middle names and academic titles may be omitted (Reason: Rule #2)
- Diacritical marks (accents and similar things) may be omitted (Reason: Rule #4)
- If transliteration is used it has to be used on the whole name, result must be 7-bit ASCII (Reason: Otherwise technical reasons are not plausible)
- In general names are handled case insensitively. If usage of different cases is very unusual or could indicate abuse, a dispute should be filed to clarify the specific case.
Examples
Allowed Variations
Name(s) in ID doc |
Name(s) in CAcert account |
Remarks |
Bärbel Renate Fröhlich |
Bärbel Renate Fröhlich |
preferred variant |
Bärbel Renate Fröhlich |
Renate Bärbel Fröhlich |
ordering of given names is arbitrary |
|
Baerbel Renate Froehlich |
Transliteration |
|
Bärbel Fröhlich |
middle name omitted |
|
Renate Fröhlich |
first name omitted |
|
Bärbel R. Fröhlich |
acceptable since two name parts (including the family name) are complete |
Dr. Bärbel Fröhlich |
Bärbel Fröhlich |
like middle names, academic titles may be omitted |
Κάρολος Παπούλιας |
Κάρολος Παπούλιας |
preferred variant |
|
Karolos Papoulias |
Transliterated according to ISO 843 |
Κωνσταντίνος Καραμανλής |
Konstantinos Karamanlis |
ISO 843, diacritical marks omitted |
Борис Николаевич Ельцин |
Boris Eltsin |
According to AcceptableDocuments this would be the "official" translation in the passport. Note that if the translated/transcribed name is contained in a ID document this translation should be preferred to manual transliteration using ISO or other rules. |
Anis Mohamed Youssef Ferchichi, artist name Bushido |
Bushido |
if an artist name is included in official ID documents it may be used in a CAcert account. |
|
Anis Mohamed Youssef Ferchichi |
of course the "official" name may also be used |
Peter de Vries |
Peter de Vries |
where: 'Peter' is the given name and 'de Vries' is the last name (preferred variant); see also Dutch usage of Tussenvoegsels; there exists no lists in the CAcert system that needs special name ordering; see also a20090618.9 on how to entering Tussenvoegsels into the system |
Paulus de Vries |
Paul de Vries |
known NL country variation (read below). Requirement: citizen of the Netherlands |
Hans-Peter Fröhlich |
Hans Fröhlich |
It is allowed but deprecated for german people. See the chapter on "Hyphen Rule" below. |
Forbidden variants
Name(s) in ID doc |
Name(s) in CAcert account |
Remarks |
Bärbel Fröhlich |
Bärbel Froehlich |
either transliteration everywhere or nowhere |
Bärbel Froehlich |
Bärbel Fröhlich |
transliteration works only one way |
Bärbel Fröhlich |
Bärbel Renate Fröhlich |
Middle name is not in ID documents |
Bärbel Fröhlich |
Bärbel F. |
Family name must not be abbreviated. Even if all names are given names, like for example in Indonesia, at least two names must be included without abbreviations (if present). |
|
Fröhlich |
If there is a given name in the docs at least one has to be used. |
Bärbel Fröhlich |
Dr. Bärbel Fröhlich |
Academic titles, like middle names, have to be contained in at least one ID document to be assured |
Bärbel Renate Fröhlich |
B. R. Fröhlich |
At least one given name must be used completely. |
Борис Ельцин |
Boris Jelzin |
not transliterated but transcribed (translated phonetically) |
William Gates |
Bill Gates |
Though a usual nickname it is not acceptable, since it cannot be found on any document. |
Matthias Beckett |
Matthew Beckett |
No translation of names |
Note: If ID documents for other alphabets also contain the name(s) in Latin characters, like many passports do, these would be acceptable even if not conforming to ISO transliteration rules, because they are contained in official documents.
Practice on Suffix
Suffixes are often a problem and leads into arbitrations, as suffixes mostly not added into ID docs. But this isn't noticed onto the join form ![]()
Despite the fact there is a link on the join form, most suffixes cannot be accepted, 'cause they are not listed in any ID docs. So the simple rule here is: prevent adding suffixes and only accept suffixes you may find in at least one ID doc.
If you find a suffix in the online account, ask the assuree, to correct his name in the online account or if once received assurance points, ask Assuree to file a dispute.
read also: Potential precedent case: a20110119.1 (... to process name change requests which are transitions satisfying the requirements of PracticeOnNames.)
Relaxed Rules
The relaxed rules follows the general strategy as defined at PracticeOnIDChecking - CCA/AP requirements
Hence, the Assurance Statement goes some distance to detune or soften the need for pure identity documents ... as long as we can reliably get the guy to Arbitration, the precise Name and Documents matter less.
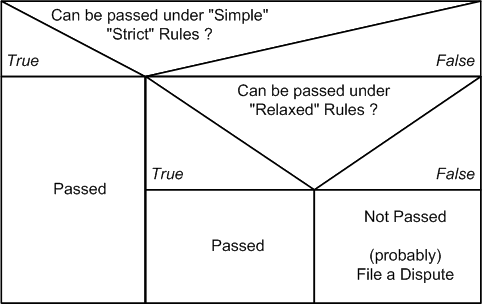
Top Down Procedure to handle Strict and Relaxed Rules
1.
First check on Strict Rules
Can case be handled under Strict Rules?
Pass, otherwise continue 2.
2.
Second, check on Relaxed Rules
Can case be handled under Relaxed Rules?
Pass, otherwise continue 3.
3.
File Dispute
Bring case before an Arbitrator
Await ruling
Relaxed Rules: Extended Assurers task
All cases that ends with Not Passed have to be passed to Arbitration or to the Assurance team for a review. Follow the simple rule: document all Names you've read an ID doc, and all names of all the ID docs you've get presented (e.g. use backside of the CAP form)
One of the requirement to allow relaxed rules is the quality in documentation by the assurers. In case of an arbitration, the Arbitrator can request required infos from the Assurer. If documentation is missing or is incomplete, the Assurer and CAcert has a problem.
Hyphen Rule
For the purposes of checking the Name against PoN, a hyphen in given names is to be treated as OPTIONAL.
The reasons for this are detailed in the Arbitration Precedents Case a20100302.1.
Since, in contrary to other countries, German custom and practice considers the hyphen as an essential part which connects two given names to one single name, German members are advised to use names in their account accordingly.
But since it is not possible for Assurers to verify every aspect of name customs it is considered acceptable to leave out the hyphen and treat two hyphenated names as different names if the member insists on it.
So acceptable variants are:
Note: CAcert can not and will not enforce every aspects of national laws and customs.
(from a20100302.1)
Further I rule, to add this sample into the PracticeOnNames as a default rule, to make the usage of hyphen in Givennames optional:
For the purposes of checking the Name against PoN, a hyphen in given names is to be treated as optional. Although under some codes of law and naming customs the hyphen is considered non-optional, it is optional under common-law tradition (cacert's family of law), and our global community has many customs. These influences push us to be more inclusive than restrictive in naming practices.
Principle regarding Assurance Statement is:
a) select the law under which Assuree / Assurer agrees to check the name local law or common law b) dependent on the law, the Assurer has to give his Assurance Statement Assurer has to accept Assuree's decision but Assurer gives his Assurance Statement. In mind, that the full name as seen in users IdDoxs is documented onto the CAP form, it doesn't causes to decrease Assurance points as it fulfills the requirements for AP and Arbitration if the Assurer has confidence into the members identity.
So acceptable variants are:
Name(s) in ID doc |
Name(s) in CAcert account |
Remarks |
Hans-Peter Meier |
Hans-Peter Meier |
Preferred variant! |
Hans Peter Meier |
optional (allowed) variant |
|
Hans Meier |
optional (allowed) variant |
|
Peter Meier |
optional (allowed) variant |
|
Peter Hans Meier |
optional (allowed) variant |
Note: CAcert can not and will not enforce every aspects of national laws and customs.
Country variations
Note the Arbitration precedent set in a20120115.2 allows for most, if not all, of the known country variations listed below - however that listing is retained as it contains useful reference material for those from outside the countries concerned.
Based on the more general case made by the Assurance Officer with the introduction of "Relaxed Rules" for assurance, I also rule that any assurer can legitimately assure a person where the name on the assuree's account does not tally exactly with their ID Documentation provided that the following conditions are met
- the assurer documents exactly the names that were seen on the assuree's ID documents
the assurer is convinced that the Account name, the assuree and the documentation all relate to the same individual and that the Account name is reasonable with respect to the assuree's name (If the names are vastly different and particularly if the account name is that of a well-known person, alarm bells should ring in the assurer's mind!)
- that the Risks/Liabilities/Obligations are disclosed to and understood by the assuree
- the assurer is satisfied that the assuree accepts the CCA
- the assurer is convinced that the assuree can be brought into arbitration if needed.
If these conditions are not met, there is the fallback option of filing a dispute for arbitration.
According to AP 2.2. Multiple Names and variations, I've set this case as a precedent under "different country variations" for Assurers
regarding AP 2.2. Multiple Names and variations
The Known Country Variations section gives advice to the Assurers, how they can handle Names according to the descriptions given in each individual section
Known Country Variations:
- NL
a20090618.12 Abbreviations on given names are allowed under the given circumstances (read ruling of case a20090618.12) advanced by ruling a20091128.2
Nederlandse Voornamen Databank
- To the Assurers:
Starting 2009 with the ATE's Assurers learned to allow only such names in Account that match the ID docs (strictly). However, as the name rules are in flux, the Dutch "roepnaam" problem hasn't been investigated deeply before the first dispute filings started. Since the ruling of precedents case a20090618.12 new infos received the Assurance Officer and also the Arbitrators about an existing Nederlandse Voornamen Databank. So on any doubt also international Assurers can check Dutch common short name variations against the name found in the ID doc. But consider, this rule is no clearance for general Nicknames. Like me, my given name is Ulrich. This is every time a problem for people from Anglo-American culture to speak, so I moved to the "Rufname" or "roepnaam": Uli. This is to read as a Nickname, because
it doesn't follow the Dutch common short name variation (country variation, that is allowed under AP 2.2), from the Nederlandse Voornamen Databank: Ulrich relates to Oldrik
- I'm not a citizen from the Netherlands, so the Dutch country variation doesn't apply
ij vs. y (digraph) - Y is a known common substitution in the dutch language for IJ (see references Netherlands Language and Languages (Alphabetical Order) and http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IJ_(digraph)) (added 2011-02-07 by AO).
- Definition: In the Dutch language, the letter combination ij is considered a single letter. It has the same value as y, and it is usually alphabetized as if it were a y.
(see also: Indonesian place name spelling issues)
- BE
As Belgium is bilingual you have to decide whether you are dealing with a Flemish firstname "roepnaam" then see the Netherland country variations. If you are dealing with French first names see the French country variations.
Please contact Assurance Officer if you have further details so we can update these infos.
- China
Personal names in Chinese culture follow a number of conventions different from those of personal names in Western cultures. Most noticeably, a Chinese name is written with the family name first and the given name next, therefore "John-Paul Smith" as a Chinese name would be "Smith John-Paul". For instance, the basketball player Yao Ming should be addressed as "Mr. Yao", not "Mr. Ming".
- To prevent missusage, a Chinese name has to be entered into the online system as defined:
- Givenname(s) into the Givenname and/or Middlenames field(s)
- Lastname / Surname into the Lastname field
- Please mark on your CAP form, which Name part is the Givenname and which Name part is the Lastname as read in an ID doc
- The resulting Names line has to be read: Givenname(s) Lastname
- If this doesn't happen in the online form, you cannot finish the Assurance, and the Assuree has to correct his name in the Online Account
- By transferring the Assurance from the CAP form to the Online form, and you read the names switched around, ask the Assuree to correct his name in his Online account or file a dispute for name correction (Givenname / Lastname switched around case)
Further readings about Chinese names: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chinese_name
- Spain
Naming System in Spain (also covers hyphenations)
Nominal conjunctions are optional. Nominal conjunctions are for better identification of surnames from other name parts. ID docs probably drops nominal conjunctions.
- The particle “de” (from)
- The particle “y” (and) (also i, e)
- Though Spanish people generally have two surnames, one surname (generally the paternal) is sufficient. Portuguese people have up to four surnames, here again one is sufficient.
- FR
- In French culture, the fullname is often written
LASTNAME, Givenname1, Givenname2, .., GivennameN
- To prevent missusage, a French name has to be entered into the online system as defined:
- Givenname(s) into the Givenname and/or Middlenames field(s)
- Lastname / Surname into the Lastname field
- The resulting Names line has to be read: Givenname(s) Lastname
- If this doesn't happen in the online form, you cannot finish the Assurance, and the Assuree has to correct his name in the Online Account
- If a name is written as LASTNAME, Givenname on the CAP form, the Givenname and Lastname part are identifiable as this is a known definition on writing names.
- But this format is prohibited in the Online form
- By transferring the Assurance from the CAP form to the Online form, and you read the LASTNAME, Givenname variant, ask the Assuree to correct his name in his Online account or file a dispute for name correction (Givenname / Lastname switched around case)
- In French culture, the fullname is often written
- GR
Deliberations on Greek givenname variations can be found under a20091231.2
- So there is a known list (may be incomplete) of common Greek givenname variations that are optional
Γεώργιος/Γιώργος -> Geōrgios/George
Ιωάννης/Γιάννης -> Ioannis/Giannis/John
Μιχαήλ/Μιχάλης -> Michael/Michalis
Ηρακλής -> Iraklis/Hercules
Θεόδωρος -> Theodoros/Theodore
Αλέξανδρος -> Alexandros/Alexander
- and I am sure there are many more examples...Γεώργιος and Ιωάννης are the two most common greek male names though.
Νικόλαος -> Nikolaos/Nicholas/Nikolas
- Indonesia
There are a couple of Indonesian name variations known. However mononyms cannot be entered into the online system yet, as the system requires givenname + lastname to be entered and prevents mononyms (givenname or lastname only)
- This issue is currently WIP in Software-Assessment and Policy Group
- Please contact Assurance team until this problem is solved for further directions
Discussion
CPS / CN
This discussion is about Assurance: matching ID documents with the names recorded in a CAcert account. What it is not about, or is less about, is what Name (if any) goes into the CN of certificates.
We will need a linking statement in the CPS that states how the names are used. Something like:
- Any Name assured to 50 points by the Assurance process may be issued in the CN of a member's certificate
- Assurance Policy may provide methods for variations for Names in the CN, such as transliterations and short forms.
Just a suggestion.
Irish Country Variation
- 3 potential variants for one name
- O'Reilly
- O Reilly
- OReilly
source: The OReilly Factor
English Language short forms of names
Applies to UK, US, AU, NZ, CA and possibly others
There is a whole set of commonly used and standard "short forms" of English forenames. Examples include "Bill" for "William" and "Dick" for "Richard". (see http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Appendix:English_given_names and http://www2.elc.polyu.edu.hk/CILL/namesmatching.htm.) These names are often used by an individual in preference to their formal names (eg "Bill Gates". At least one example is currently awaiting arbiration and a past arbitration has ruled that short forms of names are allowable under AP 2.2 a20090618.2
I believe that it is worth adding a (non-exclusive) list of names and associated short forms that are allowable under relaxed rules for name matching purposes. Currently the example "Bill Gates" for "William Gates" is specifically not allowed under "Strict" rules but it is not clear whether this would (or should!) be allowable under "relaxed" rules x1)- I personally believe that it should be allowable but (particularly for people who are not native English speakers) clarification would help! Alex Robertson
u60 - x1) read "Top Down Procedure to handle Strict and Relaxed Rules"
Advantages and Disadvantages
From former discussion about Relaxed or Strict Rules
Ruleset
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Strict
* supports possible objective of exporting identity documents to net
* supports possible objective of asserting a "r.i.g.h.t" to a name* Does not reflect current practice, therefore:
* handling of legacy accounts has to be defined
* problem to educate existing assurers, because it is stricter than some government-standard practices (e.g., Germany)
* Many problems in details have to be addressedRuleset
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Relaxed
* supports possible objective of helping members to use certs
* Simplifies creation of multiple assured accounts for the same user
* Assurers have to be educated about "official CAcert" rules of transliteration
* Rules are more complicated (at least at first glance...)
Further readings
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transliteration
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_personal_naming_conventions and http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Family_name for some background about personal names.
Arbitration Case a20090618.12: An example of an accepted country variation.
Signatures
Most Assurers aren't graphologists. Signatures may vary on daytime, may vary by using different writing utensils, may vary in a lifetime, may vary from document to document you'll check, may vary ....
So therefor, we check: the assuree signs in front of us
If there are slight differences between signature made on the CAP form and the ID documents, we don't request: "Please sign as in the ID doc" - this is unprofessional ! Ask for other documents. Bank cards, credit cards are documents, the user gets his money from the bank ....
Dates
Dates - the magic 8 numbers ... seems to be complicated to new members also to Assurers. New members, who enters their DoB into the online account and didn't noticed the missing number, as they'll enter their DoB on a recuring basis and their keyboard has a hiccup. There are many more error conditions, that makes the DoB checking a challenge of its own.
Date Formats
In the international world, we come across with several different date formats
- 12/04/2011 - the US variant
- 12-04-2011 - the UK / Commonwelth variant
- 12.04.2011 - the European variant
"XX<N>" format, where "<N>" represents years passed since the Emperor's coronation. "XX" - Japanese variant
- 2011-04-12 - the proposed format on CAP forms
As yet to be known.
As long the date can be identified clearly (12 can be a month, 4 too for above example), but in 30.03.1980 a switch between day and month is impossible, the format on the CAP form can be used freely.
Number Switches
As Assurance Policy was roled out back in Spring 2009, Arbitration discovered a raising DoB error cases. Often caused by typos:
- 01 instead of 10 - numbers switched around
- 1 instead of 15 - missing number
- 2011 instead of 1980 - current year instead of DoB year
- 12.04.2011 instead of 30.3.1980 - todays date instead of DoB
- 11 instead of 12 - number near the other number on keyboard
All these errors applies to errors on CAP forms AND all these errors applies to errors in online data !!!
The 3 Steps in Date Checking
- Check and identify the Day to Day, Month to Month, Year to Year between ID document and CAP form
Check each field value ... especialy on number ordering -> 01 .. 10
Add the month in written form behind the written date -> 2011-04-12 Apr
Frequently encountered situations
Junior Members
In principle, children or minors or juniors can also be assured. There is no minimum age set by CAcert.
Policy on Junior Assurers / Members moves to DRAFT and is therefor binding since Jan 31, 2010
There are, however, some difficulties that need to be taken into account.
- The way that persons enter into CAcert's Community is by agreeing to the CCA. This is in effect a legal contract, and in general, entering into legal contracts is for adults, not minors/juniors/children.
- This is one area where you should be aware of your country's laws, if they apply.
- In general, a minor may be able to enter into an agreement with permission of the parent or legal guardian. So you can ask for a co-signing of the form by a parent or legal guardian. However you should stress that the form is signed first by the minor, and then counter-signed by the parent.
- Treat the minor as an adult, with respect, always. One day soon, she will be.
- You will likely have to test points of understanding with both the Member and the parent.
- Acceptable photo IDs are not so useful for young people under 10.
Questions
Basically, this may result in some interesting Arbitrations. An Arbitrator may have to take into account that the CCA is not as strong in the case of a minor.
Does it make sense to assure children at infant age? The reason I'd not assure infants (let's say up to age 14) is that they protect their credentials against theft even less well than most grown ups.
Policy On Junior Assurers Members 2
Update Feb 1st, 2010: Policy on Junior Assurers / Members PoJAM DRAFT
Proposed is a ParentsKit, a CAP form related form that describes the consent and the required confirmation for becoming assured for the Junior Member. This ParentsKit should also include an informations package for the parents, what is CAcert, what does the CCA mean and so on, to be aware that the parents will understand easily what happens with the assurance. Please also add your phone number or an email address to the package, where the parents gets additional infos, where they can ask additional questions. The assurer has to make an arrangement how the signed ParentsForm receives the Assurer and the signed parents form can be returned to the Junior Member, maybe possible by snail-mail, or a second face-to-face meeting. The assurer has to notify the parents confirmation and that he has seen the signature from the parents, probably by a copy or an additional statement onto the CAP form. This procedure is for a single form carried by the Junior Member for showing to the Assurer, rather than a parent's signature over each individual CAP form.
- The Junior Member asks an Assurer to assure him.
The Assurer checks that the age of the Junior Member is in reliance to the local countries law
(eg. Germany its age is under 18 years, for other countries this may vary)- The Assurer starts a regular assurance
The first Assurer hands out to the Junior Member a ParentsKit that includes a ParentsForm and an info package.
The Parents of the Junior Member signs the ParentsForm
ParentsForm Retour
The Parents returns the ParentsForm to the Assurer by a second face-to-face meeting,
by snail-mail or by a scan of the signed ParentsForm sent by emailThe Junior Member returns the ParentForm to the Assurer by a second face-to-face meeting,
by snail-mail or by a scan of the signed ParentsForm sent by email
- The Assurer makes a note onto the Junior Members CAP form:
writes down the parental name + email
(in case of Arbitration the guardian becomes arbitration participiant instead of the junior)that he has seen the signed ParentsForm or makes a copy of the ParentsForm and adds it to the Junior Members CAP form
The Assurer now can transfer the assurance points he gave to the account with the additional (not yet existing)
checkbox that he got confirmation from the parents. x1)The Assurer returns the original ParentForm to the Junior Member for future assurances.
A scanned ParentForm is not sent back by email.
x1)
- common practice for the addtl. CCA acceptance on Assurances is to add +CCA into the locations field
- this common practice can also be used for the PoJAM acceptance i.e. +PoJAM to signal, that the acceptance from the parents exists and noted onto the CAP form
Parental Consent Form (v1.0)
- English
- German
ParentsKit
PoJAM Info for the Parents (English)
PoJAM Info für Eltern (Deutsch)
- CAcert Community Agreement
- Parental Consent Form
- All above for Printing (last updated 2010-10-11)
- English
https://svn.cacert.org/CAcert/Events/Public/PoJAM/ParentsKit_EN-1p.pdf (single paged)
https://svn.cacert.org/CAcert/Events/Public/PoJAM/ParentsKit_EN-2p.pdf (double-sided printing)
- Deutsch
https://svn.cacert.org/CAcert/Events/Public/PoJAM/ParentsKit_DE-1p.pdf (einseitiger Ausdruck)
https://svn.cacert.org/CAcert/Events/Public/PoJAM/ParentsKit_DE-2p.pdf (zweiseitiger Ausdruck)
- English
Mutual Assurance
Mutual assurance should be done where practical (AP4.2). Note that an assurance is always at the request of the Assuree and the agreement of the Assurer, so mutual assurance remains a voluntary process for both sides.
Mutual assurance has these advantages:
- it prepares non-Assurers for becoming Assurers,
- it exchanges information in a balanced fashion (sometimes known as the principle of reciprocity) and makes us more equal,
- it helps experienced assurers to pass knowledge to junior assurers about new and better practices.
There are some disadvantages:
- it can slow down the process, which will be a nuisance at booths where there are crowds.
- if the other member is not an Assurer, she may not be ready or familiar with the responsibility of keeping the CAP form safe (you may have to do that).
With an Assurer
Conducting a Mutual Assurance with another Assurer is easy, and the process is mostly left open to you and your partner-Assurer. Here are some tips.
The benefit is maximal when we help the other person to see better ways. This means that:
- giving orders on the right way to do things is not helpful
- any thing you spot should be couched in terms of differences, and not instructions
- use phrases like "I do it this way," rather than "you should do it that way."
- explain your logic for any variation. Ask her to explain hers.
- even if you know the answer, allow a journey of discovery. Instead of saying "policy X says Y," try this instead: "I wonder what policy X says?" And look it up (of course, you will need to have the copy there as well).
- do not use Arbitration as a weapon. Instead of saying "or else you'll face Arbitration," rather say this: "In the end, we might have to ask the Arbitrator to decide which way is best."
With a Non-Assurer
Conducting a Mutual Assurance with a Member who is not yet an Assurer is harder than an ordinary Assurance. But it is more valuable, because it is a really good way to train the Member towards becoming an Assurer!
To do this,
- Take an extra CAP form, or use a CAP form that is designed to be mutual (includes the same detail for both parties).
- After doing the process on the Member, ask her to take the forms and repeat the process it on yourself.
- Coach the Member as she does the steps.
- Explain why we do it that way.
Allow her to make mistakes, and then explain gently the nature of the mistake.
- Ask questions to make sure she understood what she has done.
Do not go too deep, do not get into detail. Concentrate on the essentials, and be prepared to compromise on detail. The essence is the overall feeling of the Assurance, not on getting every detail correct. Details and perfection come later with the Assurer Challenge.
Make it a fun experience, not a reminder of primary school nightmares. The goal is to make her want to take your job away
 Encourage her (we have many other jobs for experienced Assurers!)
Encourage her (we have many other jobs for experienced Assurers!)
- Once the checks over the Assurance Statement are done by her over you, she is now ready to allocate Assurance Points to you.
- She can allocate 0, 1 or 2 Assurance Points to you.
- Coach her in what the points mean.
- It is entirely up to her judgment as to how many points.
- Indeed, encourage her to be critical, and if it is her first time, issue 0 points to you. For example, if she is unfamiliar with the process, how can she be familiar with the meaning of the points?
- In this process, you yourself are not collecting more Assurance Points, but instead training a future generation of Assurer. Your mission is to teach her the best ways and understandings.
- Once she has allocated the points, have her write them onto the CAP form(s).
Because you are the Assurer, you are totally responsible for the results.
- She is not responsible because she is not an Assurer.
- You should keep the primary forms.
- If she is taking copies away, that is OK too. But advise her of the Assurer's 7 year responsibility, and write that on the form. She now holds your privacy data.
- At the moment, there is no way to enter these points into the system.
- These points will have to wait for a future system enhancement. So for the moment, the result is lost.
- But the real benefit of training remains.
- This above procedure can and will change as we get more experience.
Who keeps the CAP form?
Optional
Mutual Assurances, like all Assurances, are currently optional at the discretion of both. You may not want to do a mutual Assurance, but consider:
- you should share sufficient information with the Member to protect her. For example, your email address and Name would be a minimum. A business card would be a good idea.
Mutual Assurances are highly recommended.
Likely these things will become standard in the future (see 20090517-MiniTOP on Assurance), once Assurance Team figures out all the details. Let us know your experiences.
CAcert Assurer Reliable Statement - CARS
An Assurance is a CAcert Assurer Reliable Statement, CARS for short. It is the primary one you make to the community, as part of our overall Assurance process, or web-of-trust.
If you get involved in other, deeper parts of CAcert, you may be asked to make other reliable statements to help our processes. Here are some examples:
- reports prepared by system administrators on changes to the software are relied upon by the Board, and can be verified and scrutinised by audit.
- co-auditing involves senior assurers checking the assurance process, and making reports back to the Assurance Officer and Auditor.
- Event Coordinators are required to make sure that all Assurers at an event follow Assurance Policy, and report this back to board.
In order to signal a statement of reliance, you can add the term CARS to the end of your name. This is useful if it is not totally obvious that your statement might be relied upon.
Sample of CAcert Assurer Reliable Statement
I make a statement
My Givenname Lastname
CARS
Verification and Measurement in the Web Of Trust
To construct its global web of trust, CAcert uses a metrics system called Assurance Points to measure how well we know you.
Assurance Points
The number of Assurance Points measure how much you have been verified in Assurance processes and other approved processes, as per Assurance Policy (POLICY). They go from 0 (new Member) to 100 (fully assured Member).
- 0-49 points: "Unassured"
- This Member is not assured and her name cannot be included in certificates.
- her certificates will expire after a maximum 6 months.
- With more than 0 points, the personal details cannot be changed anymore by the Member.
- 50-99 points: "Assured"
- Each Assured Name can be added to a certificate.
- Server certificates are valid for 2 years.
- You can get a signed PGP/GPG key.
- 100 points: "Prospective Assurer"
- the maximum number of points one can get from other Assurers.
- Code signing authorisation may be requested.
You may become an Assurer by passing the AssurerChallenge
Currently points acquired do not "expire" or "decay", but this might be changed in the future.
Experience Points
Old Points |
Your Experience Points |
Issuable Assurance Points |
100 |
0 |
10 |
110 |
10 |
15 |
120 |
20 |
20 |
130 |
30 |
25 |
140 |
40 |
30 |
150 |
50 |
35 |
For every assurance, an Assurer generally gets 2 points, up to the maximum of 50 points.
Note that this system is currently unimplemented, and the experience is collected as points in the Assurance Points scheme, being points above 100. See below.
Old Points
Note: The meaning of the points has changed since the new [[http://www.cacert.org/policy/AssurancePolicy.php|Assurance Policy (POLICY)]]. The change split the old points into Assurance Points and Experience Points. Before, they were the same points system with different meanings, below and above 100 points. Below 100 the number of old points showed the amount of trust CAcert had in your identity. The points above 100 made a statement about your experience as an Assurer. Now, there are two points systems, one for each meaning. Assurance Points ONLY show how well you have been assured. Experience Points indicate how well an Assurer can do their job. The separation of Experience Points has not as yet been implemented in the online system.
What is an Experienced Assurer?
For each assurance done, an Assurer is given 2 Experience Points ("EPs"). There are also some exceptions such as 5 EPs for attending an ATE (currently its technical impossible).
When an Assurer has gained the full 50 EPs, probably by conducting 25 assurances, the Assurer is often termed an Experienced Assurer.
What is a Senior Assurer?
This is an Assurer:
- Experienced Assurer, as described above,
has attended an ATE,
- has been co-audited,
- knows CARS.
This definition was reached at the Brussels MiniTOP on Assurance.
What is a co-auditor?
A co-auditor is a very experienced Assurer who helps the Assurance Officer collect results suitable for verifying the entire system of Assurance. These results are collated for audit over CAcert.
What is a co-audited Assurance?
A co-audit or a co-audited assurance is an assurance that you the Assurer conduct over the co-auditor, see above. This is done as a Quality Assurance activity so the Assurance Officer has some means to judge the quality of the Assurer Network, as it is requires by the Audit Criteria.
During the assurance, the co-auditor checks lots of things and records the results. There is no fail for this. At the end, you should get some helpful feedback.
Co-audits are most often conducted during ATEs, so you should try and attend.
Co-Audited Assurances Results
For each co-audited assurance data is collected and stored in a database as directed by Assurance Officer. Each record includes the email address of an Assurer as a unique identifier, a collection of pass / fail / not tested results of a seasonal test set, and some context data (location, number of experience points, attendance at ATEs).
The co-audit project is initiated by DRC-A.2.y, it is instantiated into policy within TTP-Assist 5. (In coordination with internal and external auditors, the Assurance Officer shall design and implement a suitable programme to meet the needs of audit.), and is further controlled under AP 6.2 High Risk Applications.
Questions Answered
Ruling on multiple accounts
Respondent has multiple accounts.
A CAcert community member has a CAcert login account (see the Assurance Policy)
- Such an account is the link between the Member (person) and the CAcert system, and information regarding the member (like name, DoB, assurance status) is linked to that account. Although there is no rule that forbids having two or more accounts, it is not recommended, since it can cause problems.
Ruling: It is not forbidden to have multiple accounts
(Source: a20090510.3, a20110418.1)
Ruling on multiple accounts with assurer status
1 of Respondents accounts have assurer status
There is no rule that forbids a CAcert Member to have two accounts with assurer status. However, a Member with assurer status assures, and uses a CAcert account to register the assurance. Since an Assurer can only assure another member (a person) only once, it is forbidden for an assurer to assure a single person and register that assurance with more than one account. An assurer can only give the number of points linked to the account that is used to assure someone. Therefore, since having multiple assurer accounts is not required, it is strongly advised not to allow them.
Ruling: It is not forbidden to have multiple assurer accounts
Ruling: To avoid issues like this one, CAcert shall review if having multiple assurer accounts is acceptable
(Source: a20090510.3, a20110418.1)
Ruling on assuring your own accounts
Respondent assured 1 of his other accounts
Ruling: An assurer cannot meet himself/herself face-2-face. Therefore all assurances by Respondent of accounts of the Respondent are invalid and must be revoked incl. revocation of experience points.
(Source: a20090510.3, a20110418.1)
Ruling on assuring multiple accounts from one assuree
Respondents assured multiple account of one person with different assurances
Ruling: As long as each name in each account is only assured by one assurer up to the maximal number of points that the assurer may award and as long as the assurance process is followed for each assurance separately and nobody assures accounts of themselves, the AP is honoured.
Ruling: Assuring multiple accounts of the same person may not be used to excessively push the experience points of an assurer. A single occurrence of an assurance of a secondary account of an assuree cannot be seen as such a push.
Ruling: An assurer of multiple accounts from the same person should nonetheless be advised to consider the reasons why the assuree requests an additional assurance.
(Source: a20140624.1)
Id Document Photocopy is Forbidden by Default
Board motion EmailBoardDecisionsUpdateFeb2008#m20080422.3 says:
- m20080422.3 Removal of copies of ID and identification number information from archives
- Comments: CAcert when it started in 2002 required that copies of ID's were archived for 7-10 years in the archives of CAcert or archives of CAcert Assurers. In a later instance CAcert required to take note of ID numbers and/or social security numbers of the individual. For privacy reasons both (copy of ID, personal numbers) were dropped. The CAcert Assurance Programme form states that the information should be kept 7-10 years. CAcert Inc. drops the requirements for copies of ID and personal numbers and decides to remove these information from the CAcert archives and requires the CAcert Assurers who are in position of that information to do the same. The information should be deleted with care.
- Copies of ID are not needed for operational purposes and are not compliant with European privacy Directive (EU DPA).
- Decision: Accepted
- Actions: delete paper and digital copies from archive; denote the action and decision in CAcert blog; ask CAcert Assurers to follow CAcert decision. Blog on DoB and Copy IS drop done as well board order to destroy them by operators/adminsitratores has been given in May 2008.
- Further clarification:
Assurance Policy lists under 6.2 High Risk Applications:
- Additional measures may include:
- Additional information can be required in process of assurance:
- photocopy of identity documents
- Additional information can be required in process of assurance:
- Additional measures may include:
- Section 6.2 falls under the 6. Subsidiary Policies section.
- This doesn't mean, that its allowed to make a photocopy of identity documents, but maybe Subsidiary Policies can define such actions.
- Also an Arbitrator may request a photocopy of an identity document. But this are all individual events and by request.
- As section 6.2 High Risk Applications says, to take a photocopy is a High Risk Application. So therefor CAcert has decided by a board motion back in 2008 that this action is not in compliance with the EU DPA and therefor dropped it entirely.
česky | english
To CAcert.org Education & Training - To CAcert.org Education & Training Overview
To Assurance Policy - To Assurance Handbook
Some more information on CAcert
You are CAcert's "face to the customer". So you should be able to give at least some basic information about CAcert itself.
What is CAcert
CAcert is a non profit association incorporated in Australia. It is supported by a growing community of assurers (like you) who are part of a "Web-of-Trust" for identity verifications.
What is the goal of CAcert?
CAcert is a community of like-minded people working to improve our security, generally circulating around PKI technology based on x.509 "certificates" and PGP's web-of-trust.
CAcert does not have a formal or agreed mission or goal. Some of these might apply, and have been discussed from time to time:
- make security affordable and available for everyone.
- secure the Internet and increase trustworthiness.
- provide privacy through encryption.
- provide security through authentication.
For more information see the Principles of the Community.
What is the difference to other CAs?
- CAcert separates assurance (confirmation of identity) from the issuing of the certificates. Thereby the identity only has to be confirmed once to make as many certificates as needed and whenever wanted.
- CAcert is a "non-profit" community of volunteers. It is independent from commercial CA's.
- Some CAs issue free certs, and some use a WoT, but they tend to only issue low-level client certificates, but no server certificates or strongly verified certs. These free certs are intended to drive you to their CA so they can sell you higher value products. There is nothing wrong with that (your supermarket does the same thing) but it might not be appropriate to your needs.
Arbitration
Arbitration is CAcert's main channel for dealing with anything unexpected or unusual that might go wrong. This includes complaints about inappropriate conduct of an Assurance, invalid or inappropriate data in any member account, or inappropriate usage of certificates, but also unclear policies or practices. Indeed, just about anything may be disputed, and the policy documents often defer difficult issues by simply saying file a dispute. In this way, the policy documents and Arbitration work hand-in-hand: Policy handles the expected and the easy; Arbitration handles the unexpected and the hard, and both of them together provide the foundation for all work done in CAcert.
As a part of accepting the CAcert Community Agreement (CCA), every member accepts Arbitration according to CAcert's Dispute Resolution Policy (DRP). Anyone who has a complaint about anything relating to CAcert may file a Dispute by sending a mail to mailto:support@cacert.org. You will be notified of any dispute via your primary email address, so you are required in CCA to keep this working.
How does Arbitration work?
Once a dispute is filed and notified, an Arbitrator is chosen by CAcert from amongst our own senior and experienced Assurers. Arbitrators are strongly familiar with the policies, rules, principles, customs and specialties of CAcert. As an Assurer, you should be somewhat familiar with the rules, and at the least, know where to find them so as to answer basic questions from members.
The process of an Arbitration is this, in brief:
the Arbitrator looks at the situation by means of evidence,
- applies the policies and rules, and if necessary the law (of NSW, Australia), and
- delivers a ruling.
The ruling is binding on you, all members, and CAcert itself. It is generally published so that all the Community can watch and govern the system, and we can improve our policies and practices over time.
As we use Arbitration for all sorts of unusual and difficult questions, being named in an Arbitration is no bad thing, in and of itself; indeed, it is a mark of experience to participate. One day, you may be asked to sit as an Arbitrator, and this will likely require you to have been named in Arbitrations already. You can find more details and many references at our ArbitrationForum.
Background to Alternative Dispute Resolution
CAcert has introduced Arbitration as a protection for its members.
Normally, if something goes terribly wrong, you might be dragged into a civil court to face a lawsuit. Especially, as CAcert provides certificates making statements about people across the world, it is highly likely that any lawsuit would be filed in a country far away. In your country, the system of justice may have a reputation for looking after you, but this is not true of all places. At a minimum, remote systems of justice will be difficult and expensive for you to understand and navigate, even if they are fair. As well, there will be expensive lawyers, and you may be hit with a harsh judgment that does not fully appreciate what certificates are about and what we as a Community are about. Even if the court rules in your favour, it could be a Phyrric victory, one that you could not afford.
Therefore, instead of using the courts, we agree to deal with all our disputes internally. The authority for this is found under the Arbitration Act in each country, and in the clause in the CCA:
3.2 Arbitration as Forum of Dispute Resolution You agree, with CAcert and all of the Community, that all disputes arising out of or in connection to our use of CAcert services shall be referred to and finally resolved by Arbitration under the rules within the Dispute Resolution Policy of CAcert (DRP => COD7). The rules select a single Arbitrator chosen by CAcert from among senior Members in the Community. The ruling of the Arbitrator is binding and final on Members and CAcert alike.
You should be familiar with that clause and how to explain it to new and prospective Members.
Most countries have Arbitration Acts in place as law (see for example the German Arbitration Act (The text of this act, entered into force on 1998-01-01, is integrated into the Code of Civil Procedure, Book 10, Article 1025 ff)) that permits and even encourages internal Arbitration such as ours. This makes sense where a local or specialised community might have a better understanding of their own conventions and rules, where international affairs make it impractical to choose a neutral or cost-effective court, and where the real natures of the disputes do not justify the expense of the courts (and especially the lawyers).
These aspects are a natural fit for CAcert because we are in a complex international environment of Assurances, the Internet and certificates. The Arbitration Act provides us with a way to deal with any disputes internally, rather than going to courts, which likely are in far away countries, involve expensive lawyers, and have little knowledge of the process of certificates. Hence, we achieve a balanced and cost-effective legal approach across the entire Community, which applies to you as well as every other member, and to CAcert itself.
In the event of any lawsuit filed against you in relation to your CAcert activities, you should ask the court to refer the case back to Arbitration, citing the above clause and Act. There is no guarantee that a case will be so referred, and criminal cases are not referred, but as a matter of public policy courts will routinely refer cases back to Arbitration where this was the agreement.
The intent is to protect you and all members. This means that, in order to protect other members, an Arbitration case may result in some penalty imposed upon you if the Arbitrator finds that you were acting against CAcert's policies, rules and/or principles! See DRP section on remedies for more details.
How is privacy protected?
- Forms stay with the assurer and are only forwarded to CAcert under special circumstances.
- From the outside it is not evident who assured whom, the online system keeps that information private.
- CAcert will not give any data to third persons or third parties, except when ordered by an Arbitrator during dispute resolution.
For more details look at the privacy policy and also the last section of the Assurance Policy 7. Privacy.
Is CAcert included in browsers by default?
Please see: InclusionStatus
How many people use CAcert?
- for current data, go to the website, click on About CAcert.org at the right, then on CAcert Statistics. Do this manually, the link isn't published because the statistics collection is live and this slows the server down a lot.
Some technical aspects
While assuring people they may ask you some technical questions. Just to help you to pose as a real crack, here are some basics. ![]()
What are public and private keys?
"Public key cryptography" works with pairs of public and private keys. Each key in the pair can be used to encrypt data that can be decrypted only by someone with the other key. By convention, one of the pair is designated the "public key", and the other is designated the "private key".
The private key is kept secret and protected. It is never shared.
The public key is made available as broadly as possible since this is the one that can be used to encrypt data that only the owner of the private key can decrypt. It also allows decryption of data which has been encrypted by the private key.
So if you want to send someone an encrypted message you need your partner's public key. If you loose your private key you cannot decrypt messages sent to you any more.
By encrypting a document's hash value with your private key you can create a digital signature, which everyone can verify using your public key.
The public part of the key can be created from the private key (really?), but the public part does not allow anyone to guess the corresponding private key. Or better, it is really very very hard to guess the private key from the public part if the private key is "big enough".
What is a digital signature?
A digital signature is a kind of "seal" attached to a document that guarantees that the signed document has not been changed since the creation of the signature and it guarantees that it was created by someone who has access to the corresponding private key.
Technically speaking it is a hash value of the document encrypted by the private key of the signer. There are many different ways to implement this.
What is a certificate
A certificate in this context is a "document" containing a public key, some information about the owner of this key, and a signature from a Certification Authority ("CA").
Certificates following the X509 standard (including those issued by CAcert) contain issuing and expiry dates, hashes (or "data fingerprints") used to validate the certificate, and a unique serial number. In addition, certificates generally include some information about the user, such as the name or email address.
What can I do with a certificate?
Typically, the certificate represents a claim made by the CA over the "subject" of the certificate, e.g., an individual or organisation. A CA defines the exact meaning of a certificate in its documentation. For example, who can get one, what checks are made, and what you can do with this information. In order to know what to do with a certificate, you should examine the documentation carefully:
the "Certificate Practice Statement" (CPS) generally states the meaning of the certificate and what checks are made to support this meaning. In theory, you should examine a CA's CPS very closely before deciding what to do with any given CA's certificates. For CAcert, look for the relying party statement and then look at the Assurance Policy to see what the source of that information is.
the "Relying Party Agreement" (RPA) is where the legal info is, and in particular whether you have the right to do so. For CAcert, this is the CAcert Community Agreement.
errrr ... the certificate certifies something, the "subject" of the certificate. Ordinarily this is the e-mail address of the owner, and name if s/he has enough assurance points, or the web address/domain of a web server. The last sentence of the previous paragraph makes it seem that both e-mail address and name are optional for a client certificate, when in fact at least one should be there, otherwise what is the certificate certifying?
[iang] ... the assumption that the certificate "certifies" something has to be treated with care. What does that mean, and who can rely on that? I've tried to unravel this from the contents of the certificate, above. The other question of whether there is a use for a "null certificate" or one without name or email address ... then becomes easier to deal with. For CAcert's case it is somewhat irrelevant, and this would make a good CATS question ![]()
What can I do with certificates issued by CAcert
Secure web servers
You can generate certificates for https servers. Though at the moment CAcert's root is not included in standard Mozilla and Internet Explorer, it is already included in several Unix-like distributions.
And it's easy to install CAcert's root certificates manually.
X509 Client certificates
These can be used to encrypt and/or digitally sign emails. See ClientCerts for our growing list of places you can yse your client cert. They may also used as a way of authenticating with web servers, like the certificate login on CAcerts website or VPN servers.
Code signing and IDN certificates
If you are an Assurer, you can get certificates signed/issued by CAcert for code signing and IDNs (International Domain Names).
Due to the increased possibilities for abuse those certificates have additional requirements. The CPS states that this requires Assurer level, which you meet if you are reading this Handbook. However note that as of 20091106, there is a move to reduce these requirements. Watch this space.
OpenPGP signatures
Get your PGP keys signed by CAcert's key. This should considerably increase the trust in your PGP key since many people trust CAcert's signature.
Does CAcert use OCSP?
CAcert offers online certification verification via the Online Certificate Status Protocol. Whether your applications actually use it, is another question.
Where can I get more help with technical problems
Best places for technical help are the wiki and IRC, see the #Appendix below.
Appendix
Help & Support
In order to advise users on their options, you should know about these:
- mailing list cacert-support /at/ lists.cacert.org
- support (at) cacert.org .
documentation located at the CAcert wiki: http://wiki.cacert.org/
- Chat/IRC forum at: irc.cacert.org
- #cacert english channel
- #cacert.ger german language channel
SSL version (prefered) https://irc.cacert.org/ non-SSL version http://irc.cacert.org/
- If you do not know how to use an ircclient you may also try the CAcert Web IRC or Webchaton
Support is maintained by the Support Team, as directed under Security Policy Section 8. The Channels of support are listed in the Security Manual.
- As an Assurer, you should consider joining the support mailing list and helping out. Or, hang around the IRC chat room.
Inputs & Thoughts
YYYYMMDD-YourName
Text / Your Statements, thoughts and e-mail snippets, Please